Automated Structured Data Extraction from Intraoperative Echocardiography Reports Using Large Language Models
Key Points
Large language model ensembles automatically generated clinically useful perioperative transesophageal echocardiography data (left ventricular ejection fraction, right ventricular systolic function, & tricuspid regurgitation) from unstructured text contained in reports.
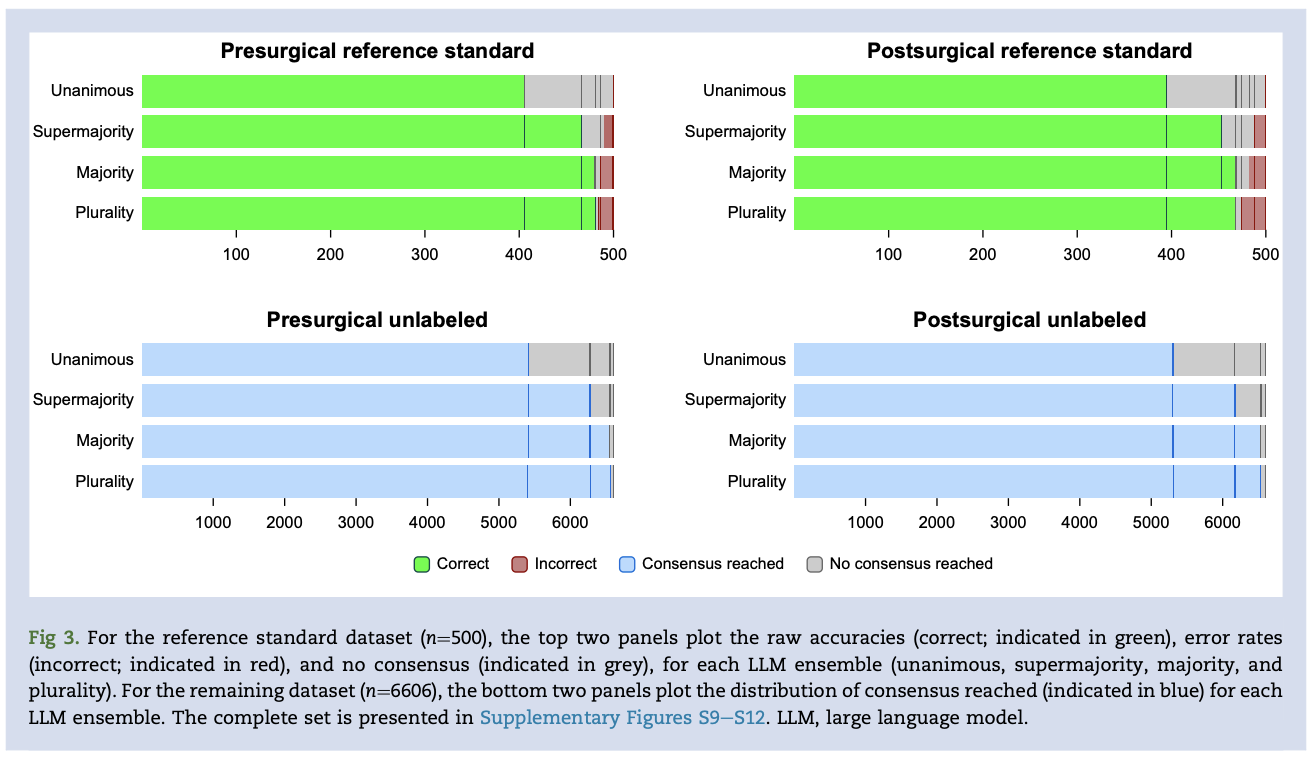
The unanimous LLM ensemble achieved the highest consensus accuracies (99.4% presurgical; 97.9% postsurgical) and the lowest error rates (0.6% presurgical; 2.1% postsurgical) but had the lowest data extraction yields (81.7% presurgical; 80.5% postsurgical) and the lowest raw accuracies (81.2% presurgical; 78.9% postsurgical).
The plurality LLM ensemble achieved the highest raw accuracies (96.1% presurgical; 93.7% postsurgical) and the highest data extraction yields (99.4% presurgical; 98.9% postsurgical) but had the lowest consensus accuracies (96.7% presurgical; 94.7% postsurgical) and highest error rates (3.3% presurgical; 5.3% postsurgical).